|
Electrostatics
Objectives
• Know that there are two types of electrical charges
• Know that negative charges are small and light, and
that charges can be transferred by friction.
• Be able to describe and explain processes involving
the transfer and interaction of charges, using correct technical
language.
Task 1
Remind the person next to you:
• What are the two types of electrical charge?
• How could someone become charged with static
electricity?
• What does the word static mean?
Can you think of somewhere the word static is used which
is not referring to electricity?
• Which type of charge is small and light?
(hint: think about your work on atomic structure in chemistry lessons!)
Task 2
Think about a time when you have had a shock from
static electricity. What were you doing at the time? What
could have caused the static shock? Your teacher will ask some of
you to share your ideas with the class, and show you the simulation
below, which helps explain how static shocks occur.
n.b. there is also a local copy stored
here.
Task 3
Look at the simulation below, which shows how two
insulators can be charged by rubbing them against each other. In
this case, a balloon is charged up by rubbing it on a jumper.
n.b. there is also a local copy stored
here.
Task 3
Complete the sentences below:
|
The two types of charge are ___________ and __________.
__________ charges are much smaller and lighter than
_________ charges.
Charges can be transferred between insulators by
_________.
If an object has _________ numbers of ________ and
_______ charges it is 'uncharged' or 'neutral'.
An object with an ________ of positive charges
is 'positively charged', and an object with an excess of ________
charges is negatively ________.
Opposite charges __________ and like charges ___________.
|
Now copy and complete the table:
|
|
Combination of charges |
Attract or repel? |
| positive and
positive |
|
| negative and
negative |
|
| positive and
negative |
|
|
Task 4
Write an explanation of what happens when a balloon is charged up by rubbing
it on a jumper. Use the following terms in your explanation:
charge
positive negative
neutral uncharged
equal transfer
friction charged
light small
build-up gained excess
lost deficit insulator attract
Task 5
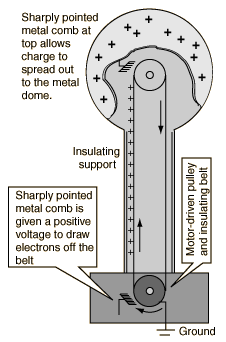
Your teacher will demonstrate a Van de Graaff generator,
which is very effective at transferring charge.
|
Listen carefully as your teacher explains how the Van de
Graaff generator works.
Your teacher may show you some of the following
demonstrations:
-
A person being charged up.
-
Sparks jumping from one person to another.
-
A stack of foil pie cases being charged up.
-
Soap bubbles being repelled.
|
 |
|

